Explore our roof anchors
Rope Descent System (Direct Rigging) vs Suspended Platform

Rope Descent System - Requirements
A Rope descent System is the most cost-effective window washing solution.
When designing a rope descent system, there are a lot of considerations to keep in mind.
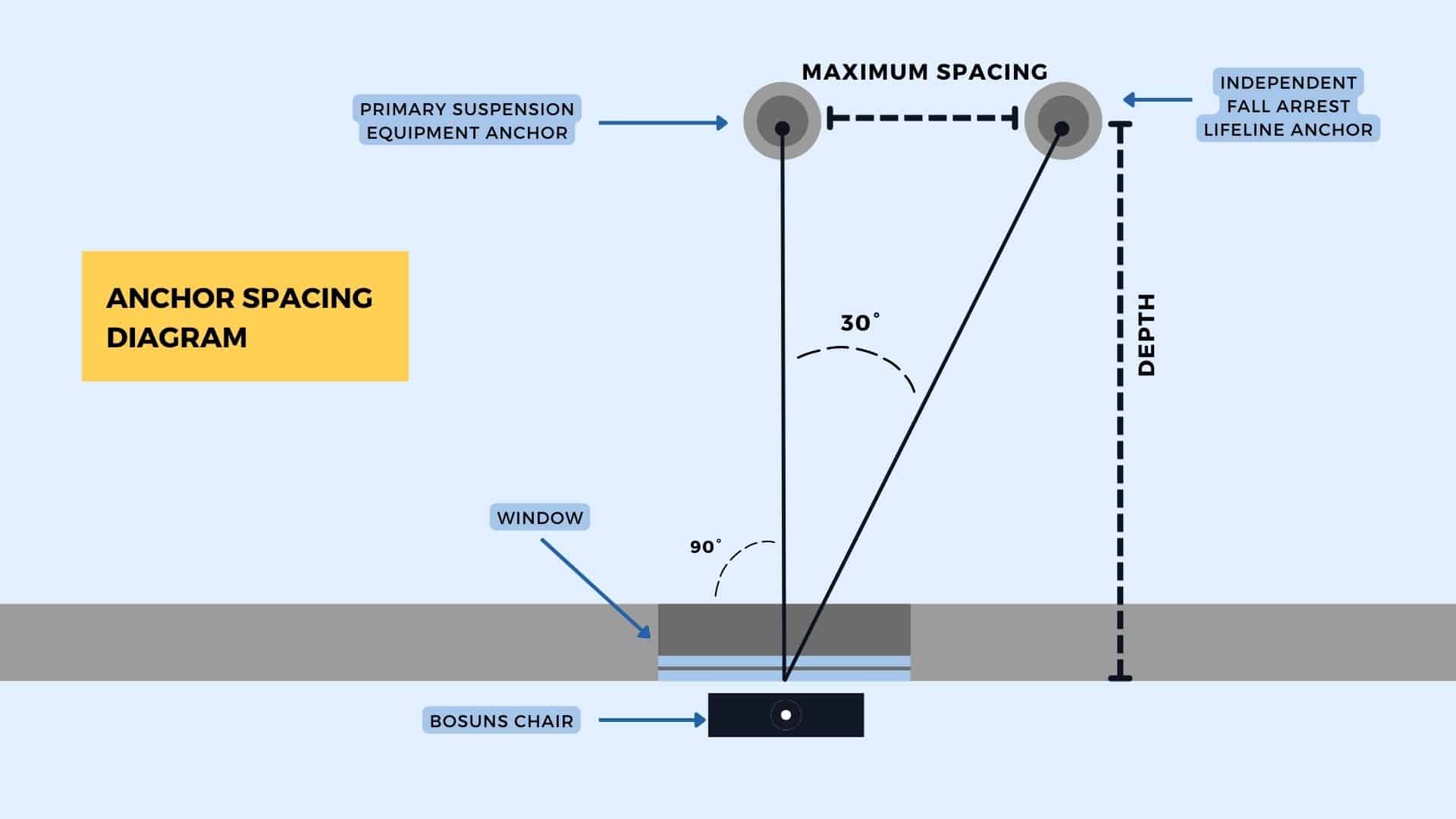
1. The offset degree
Permanent roof anchors are positioned in line with the point of suspension while maintaining an offset degree to the safety line. The suspension tie-off anchor point and the lifeline tie-back anchor point need to be distanced by the offset degree. The required angle between them differs by region, but it’s usually either 25 degrees or 30 degrees throughout North America.
2. Anchors points for both safety and suspension
Two anchor points are needed to accommodate both the suspension and safety lines. The spacing between them depends on the building’s dimensions.
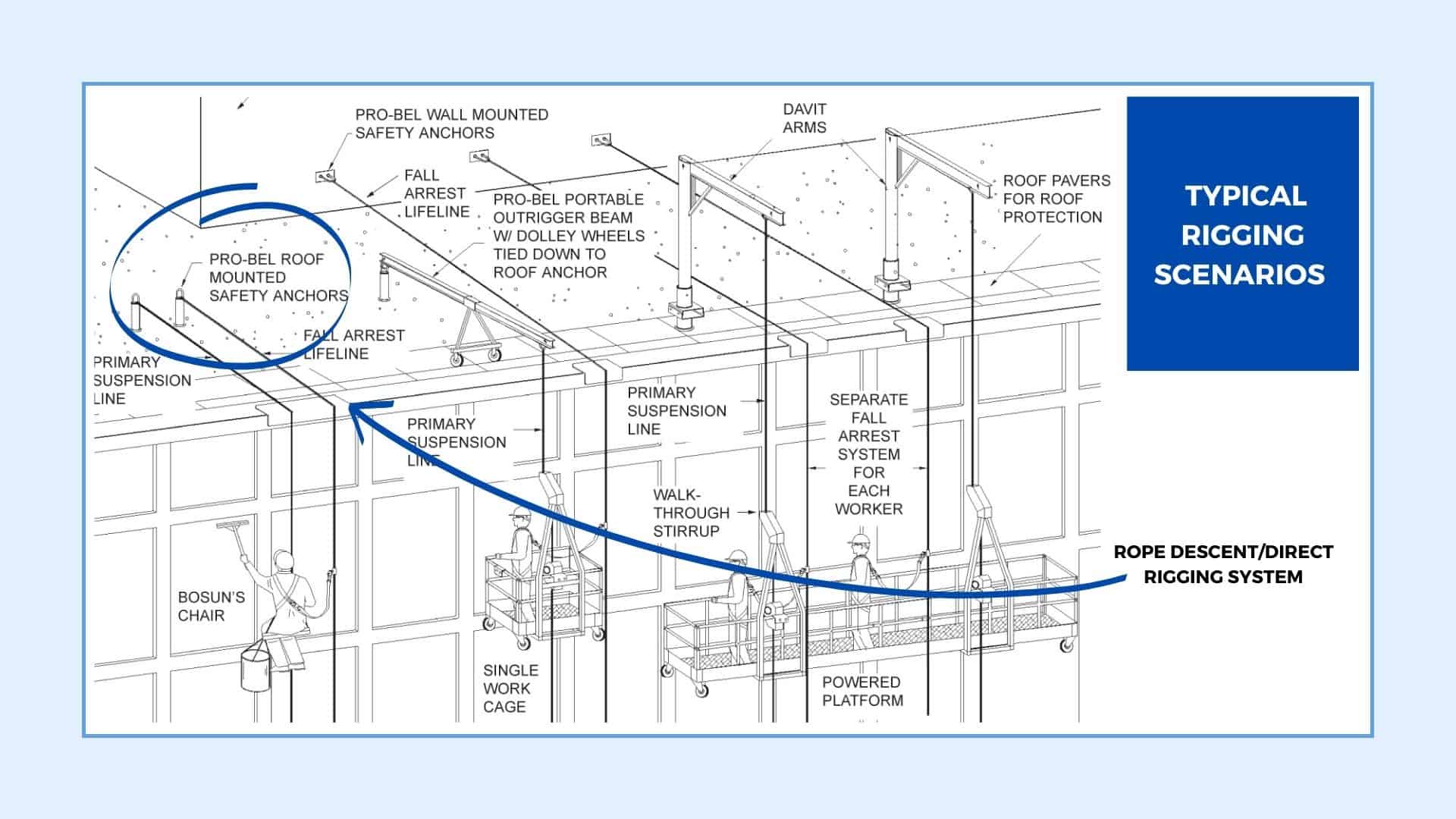
An illustration of the most common rigging scenarios, including direct rigging with Pro-Bel roof anchors.
3. The Parapet/building’s edges
The parapet/building’s edge needs to be designed to take the following applied loads:
- 310lbs working load
- 900lbs Fall Arrest Load
- 1800lbs Factored Fall Arrest Load
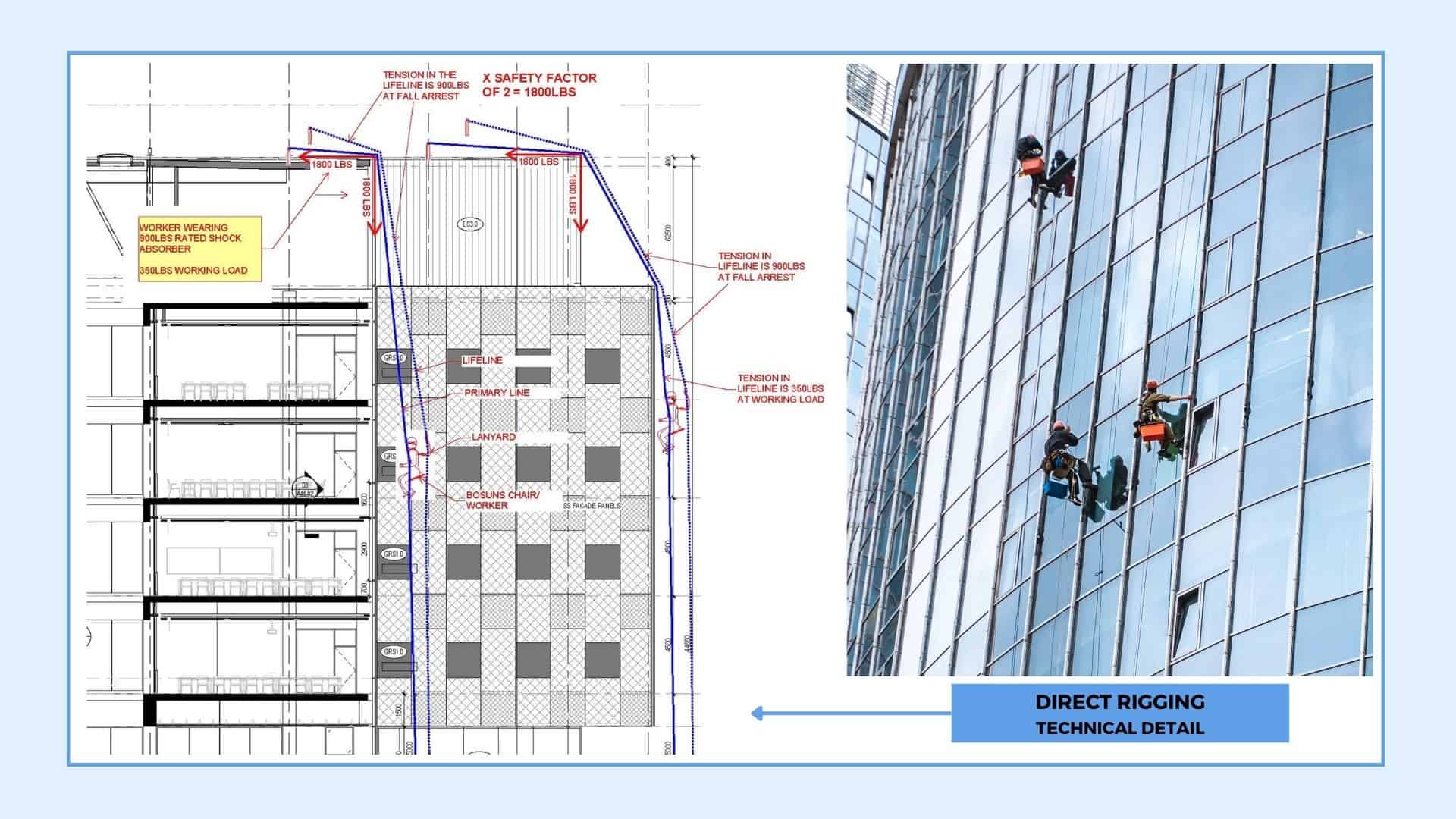
A technical detail of direct rigging load requirements.
4. Working around a non-structural parapet
If the building’s parapet is non-structural, a workaround must be implemented to ensure no load is applied. Davit arms or outrigger beams must be installed to avoid damaging the parapet.
5. Gap detail
If there is a glass railing, a gap detail might be requested to avoid window washing davits or outrigger beams. The system placed will have to be fully customized.
We've also made our gap details available for download; check out our blog on gap details that every architect should know.
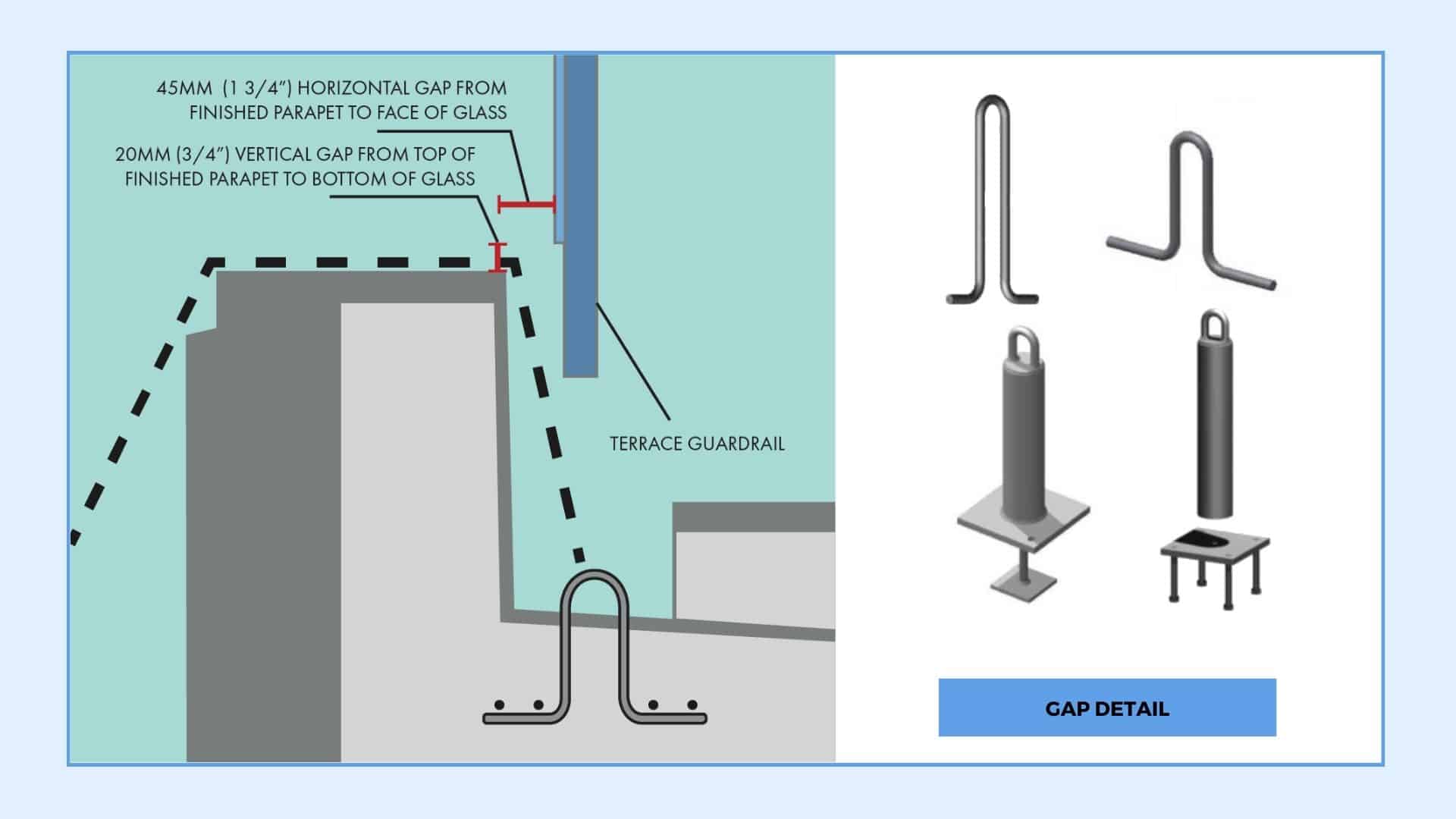
An illustration of the gap detail we often ask for in order to accommodate a rope descent system.
What if a building is over 300ft?
If a building’s drop height is over 300ft, a suspended platform is required. Davit systems are usually incorporated unless there’s some form of architecture that would render them an ineffective solution.
Window washing davits are spaced approximately every 20ft with tie-back anchors placed between or behind the suspension system for vertical lifelines to be placed.
Window washing davits are more costly than roof anchors, given that the equipment is a lot more expensive to manufacture, shipping costs are higher, and installation takes a longer time. However, to comply with OSHA, davit systems are the suggested window washing solution for high-rises over the required height.
What if a building is over 492ft?
If buildings have a vertical drop exceeding 492ft, they are required to install a powered roof car, also known as a BMU, to conduct window washing or facade maintenance. Powered roof cars are the most expensive form of window washing equipment given they’re fully mechanized and customized to meet the building’s needs.
Sometimes, areas on skyscrapers have vertical drops that don’t exceed the 492 feet threshold. For these sections of the building, traditional window washing safety systems can be incorporated into the design.
Share this Post